To understand the way in which Earth and space are connected from an environment and sustainability point of view, it is necessary to go back in time. In September 2015, more than 150 leaders met at the UN to discuss about important topics such as global development, people’s well-being promotion and environmental safeguard. The result was the creation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development which is made up of 17 Goals to be achieved within 2030.
And now “space” comes into play, indeed some of these Goals are reachable thanks to it too. The covering of the observation satellites, the same that back when no one would have imagined discovered the ozone hole, offers a unique and privileged perspective on our planet, allowing to examine its “health condition”.
Let’s discover more in detail their precious help and how spatial research contributes towards sustainability.
#Goal 2: End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture
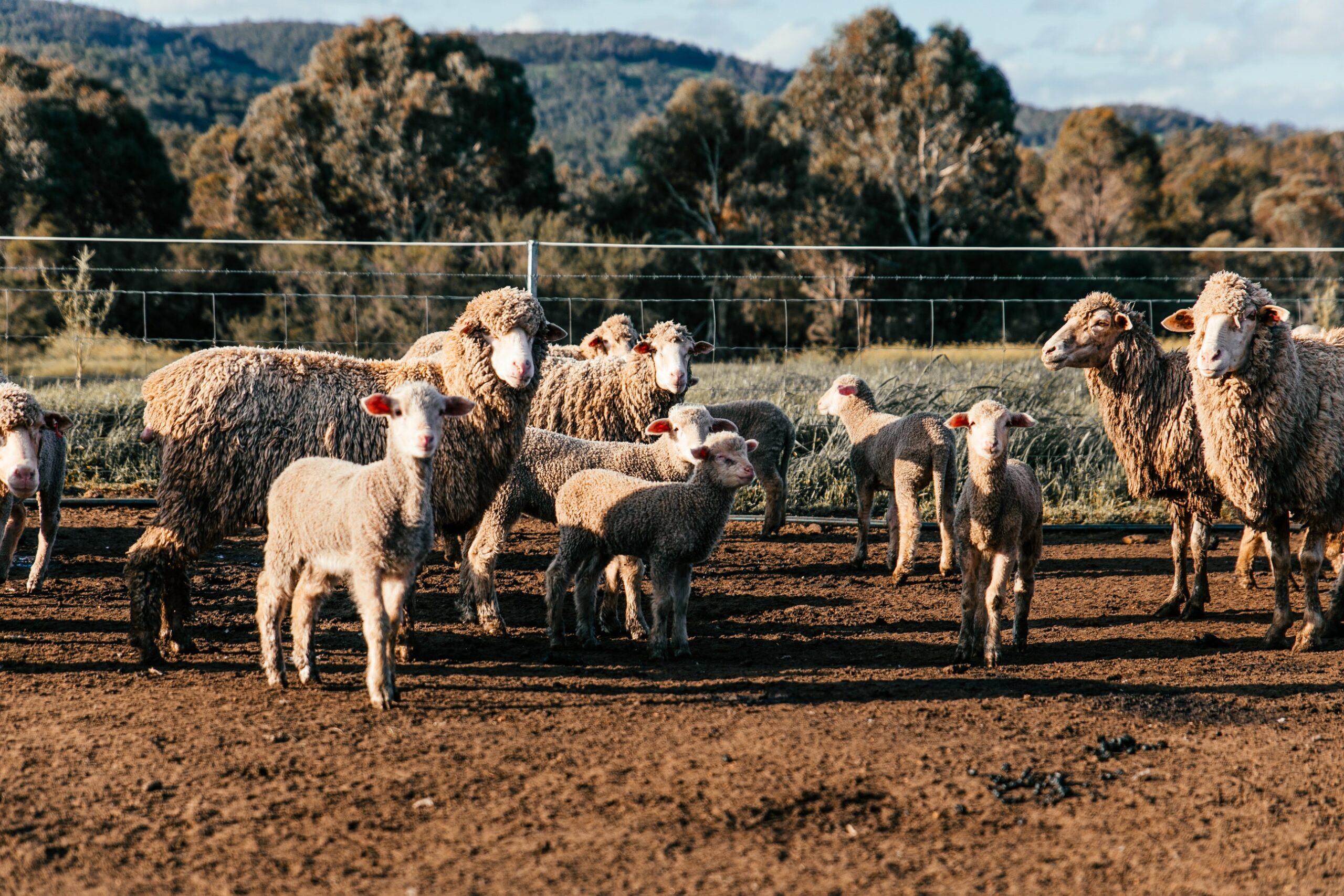
Agricultural lands represent 37% of the total global surface, for this reason satellites are essential allowing to collect data of a so extended area. Through the images coming from these instruments, farmers are able to decide when and how much they should irrigate and fertilize and when it is the right moment to harvest. Moreover, using specific disposals it is possible to measure the strength of the crops and their productivity.
#Goal 13: Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
In many cases the earliest and even the most evident signs of the climate change can be observed and registered in remote areas of the Earth. Satellites allow the constant global deforestation monitoring, the water pollution levels, the glaciers conditions and the desertification. In this way it is possible to act from our planet trying to ward these events off or at least to minimize them.
#Goal 14: Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development
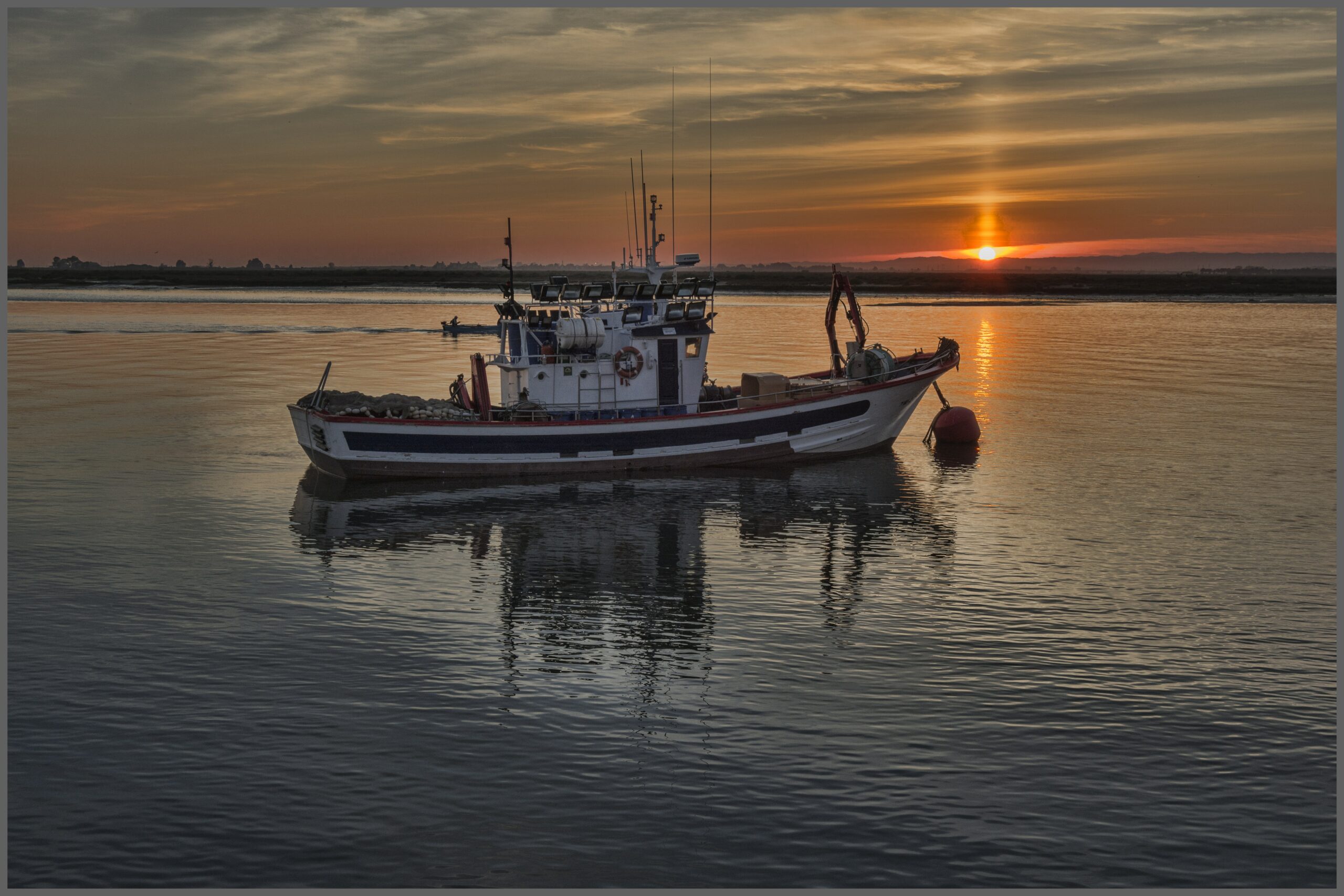
Through the advanced technology of the satellites, it is possible to trace and inform the competent authorities of illegal fishing cases.
#Goal 15: Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss
Thanks to satellites, natural habitats can be monitored, and identifying the development and destruction indicators it is possible to accordingly act.
Therefore, we could compare the spatial research to a real inspector, who is able to see everything from the above sending in real time information and alerts in the case in which anything is not going in they way in which it should!